
JWT Authentication in Spring Boot with Kotlin: From Zero to Production
Learn how to implement secure JWT authentication in Spring Boot with Kotlin, from basic setup to production-ready deployment.
Introduction
JWT (JSON Web Token) authentication is a stateless authentication mechanism widely used in modern web applications. This guide will walk you through implementing a production-ready JWT authentication system in a Spring Boot application using Kotlin.
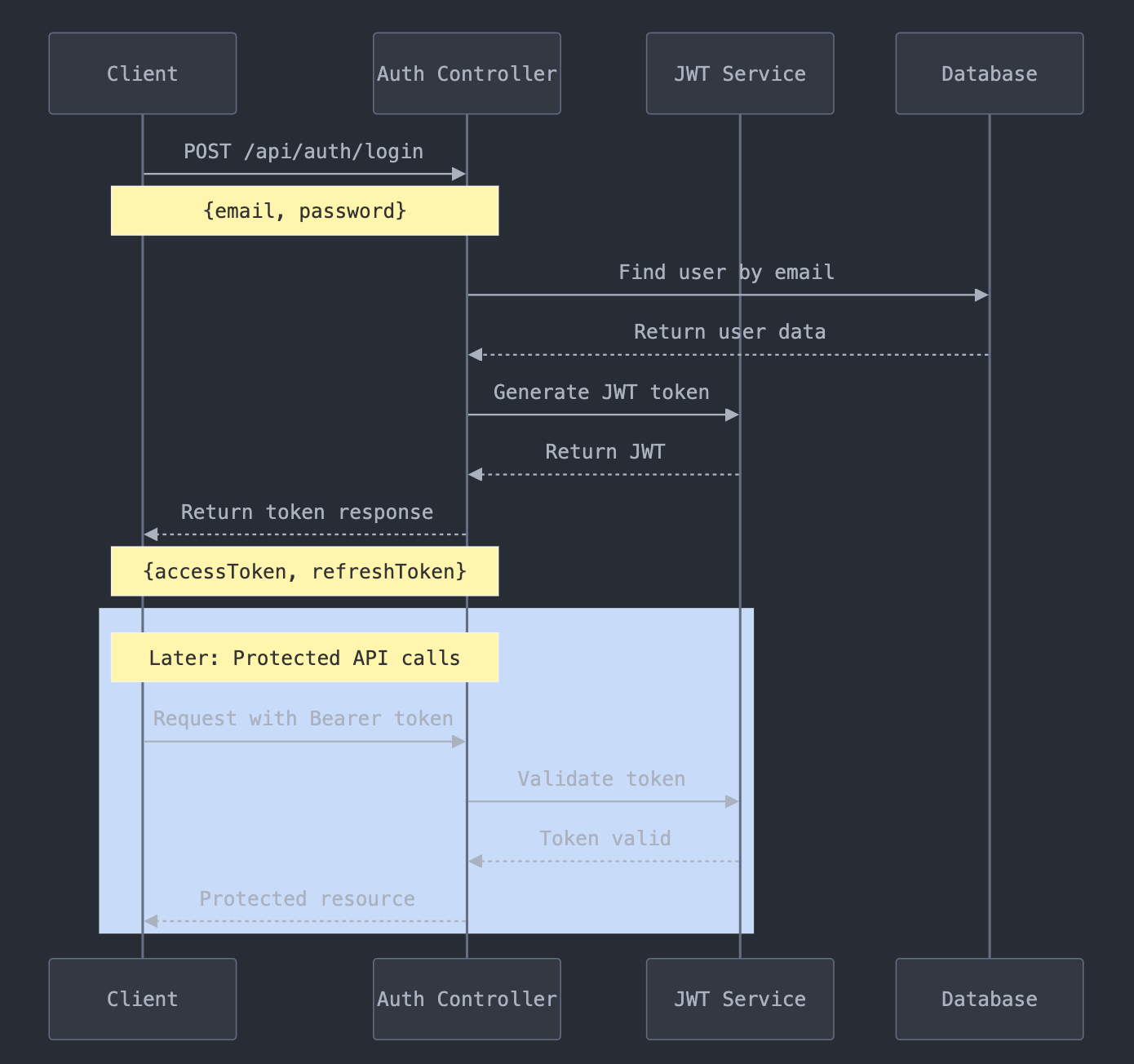
By following this tutorial, you will:
- Understand how JWT authentication works
- Set up a Spring Boot project with Kotlin and necessary dependencies
- Implement user registration and login
- Create and validate JWT tokens
- Secure your endpoints with JWT authentication
- Add refresh token functionality
- Implement best practices for production deployment
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you will need:
- JDK 17 or later installed
- An IDE (IntelliJ IDEA recommended)
- Basic knowledge of Kotlin and Spring Boot
- Gradle or Maven for dependency management
- (Optional) Postman or similar tool for API testing
Step 1: Project Setup
First, let's create a new Spring Boot project. You can use Spring Initializr (https://start.spring.io) with the following dependencies:
- Spring Boot Starter Web
- Spring Boot Starter Security
- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA
- PostgreSQL Driver
- jjwt-api (for JWT handling)
Here's the complete build.gradle.kts configuration:
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.tasks.KotlinCompile
plugins {
id("org.springframework.boot") version "3.2.1"
id("io.spring.dependency-management") version "1.1.4"
kotlin("jvm") version "1.9.21"
kotlin("plugin.spring") version "1.9.21"
kotlin("plugin.jpa") version "1.9.21"
}
group = "com.example"
version = "0.0.1-SNAPSHOT"
java.sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation")
implementation("com.fasterxml.jackson.module:jackson-module-kotlin")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-reflect")
// JWT Dependencies
implementation("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-api:0.12.3")
runtimeOnly("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-impl:0.12.3")
runtimeOnly("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-jackson:0.12.3")
// Database
runtimeOnly("org.postgresql:postgresql")
// Testing
testImplementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test")
testImplementation("org.springframework.security:spring-security-test")
}
tasks.withType<KotlinCompile> {
kotlinOptions {
freeCompilerArgs += "-Xjsr305=strict"
jvmTarget = "17"
}
}
tasks.withType<Test> {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Step 2: Setting Up the Database Models
Let's create our user model that will store authentication information. Create a new file User.kt:
package com.example.auth.model
import jakarta.persistence.*
import java.time.Instant
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
data class User(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
val id: Long? = null,
@Column(unique = true)
val email: String,
val password: String,
val firstName: String,
val lastName: String,
@Column(nullable = false)
val createdAt: Instant = Instant.now(),
@ElementCollection(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@CollectionTable(name = "user_roles", joinColumns = [JoinColumn(name = "user_id")])
@Column(name = "role")
val roles: Set<String> = setOf("ROLE_USER")
)
data class RefreshToken(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
val id: Long? = null,
@OneToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id", referencedColumnName = "id")
val user: User,
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
val token: String,
@Column(nullable = false)
val expiryDate: Instant
)
Step 3: Implementing the JWT Service
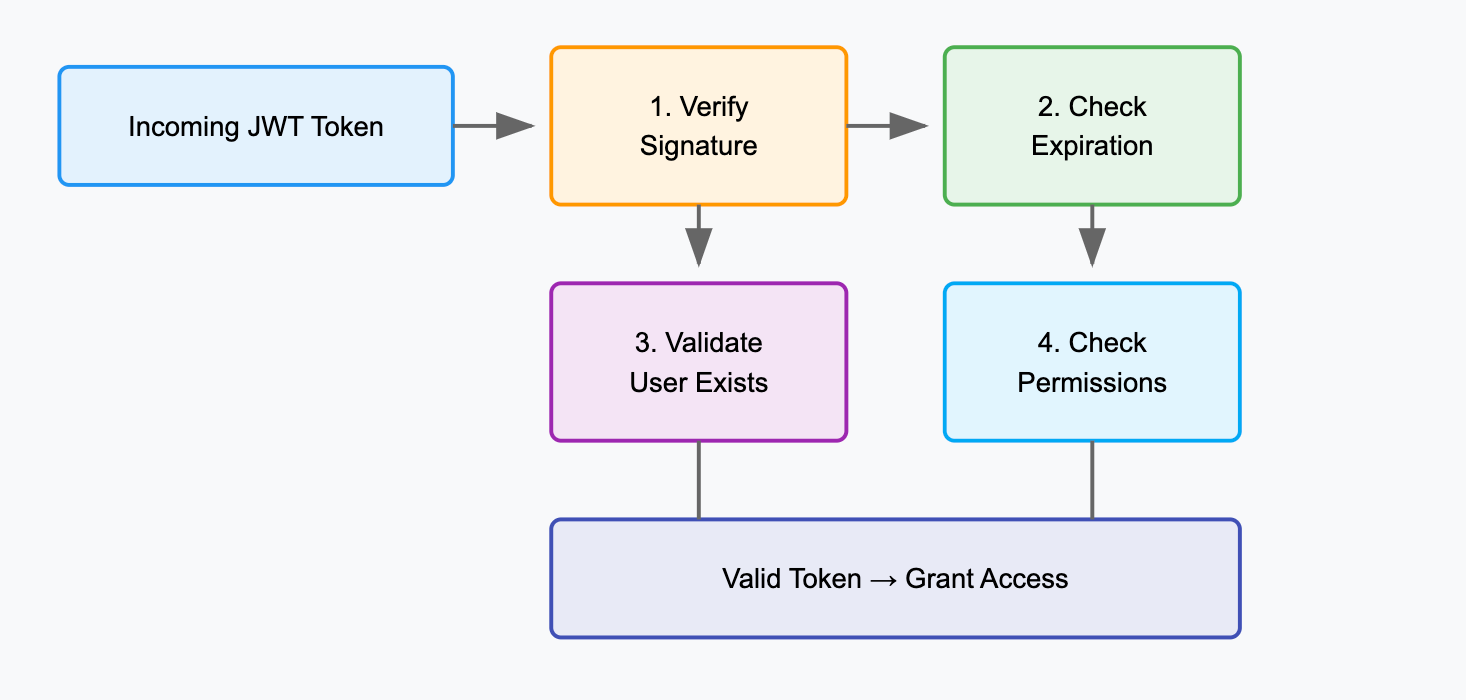
Create a service to handle JWT token generation and validation.
package com.example.auth.service
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import java.security.Key
import java.util.*
@Service
class JwtService {
@Value("\${jwt.secret}")
private lateinit var secret: String
@Value("\${jwt.expiration}")
private lateinit var expirationTime: String
private val key: Key by lazy {
Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(secret.toByteArray())
}
fun generateToken(userDetails: UserDetails): String {
return Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(userDetails.username)
.claim("roles", userDetails.authorities.map { it.authority })
.setIssuedAt(Date())
.setExpiration(Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expirationTime.toLong()))
.signWith(key)
.compact()
}
fun validateToken(token: String, userDetails: UserDetails): Boolean {
val claims = extractAllClaims(token)
val username = extractUsername(claims)
return (username == userDetails.username && !isTokenExpired(claims))
}
private fun extractUsername(claims: Claims): String {
return claims.subject
}
private fun isTokenExpired(claims: Claims): Boolean {
return claims.expiration.before(Date())
}
private fun extractAllClaims(token: String): Claims {
return Jwts.parserBuilder()
.setSigningKey(key)
.build()
.parseClaimsJws(token)
.body
}
}
Step 4: Security Configuration
Configure Spring Security to use JWT authentication:
package com.example.auth.config
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class SecurityConfig(
private val jwtAuthenticationFilter: JwtAuthenticationFilter
) {
@Bean
fun securityFilterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http
.csrf { it.disable() }
.authorizeHttpRequests { auth ->
auth
.requestMatchers("/api/auth/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
}
.sessionManagement { session ->
session.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
}
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter::class.java)
return http.build()
}
}
Step 5: Creating the Authentication Controller
Implement the authentication endpoints:
package com.example.auth.controller
import com.example.auth.dto.LoginRequest
import com.example.auth.dto.RegisterRequest
import com.example.auth.service.AuthService
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/auth")
class AuthController(
private val authService: AuthService
) {
@PostMapping("/register")
fun register(@RequestBody request: RegisterRequest): ResponseEntity<AuthResponse> {
return ResponseEntity.ok(authService.register(request))
}
@PostMapping("/login")
fun login(@RequestBody request: LoginRequest): ResponseEntity<AuthResponse> {
return ResponseEntity.ok(authService.login(request))
}
@PostMapping("/refresh")
fun refreshToken(@RequestBody request: RefreshTokenRequest): ResponseEntity<AuthResponse> {
return ResponseEntity.ok(authService.refreshToken(request))
}
}
Step 6: Production Considerations
When deploying to production, consider implementing these security best practices:
- Secure JWT Secret Management:
# application.yml
jwt:
secret: ${JWT_SECRET:your-256-bit-secret}
expiration: ${JWT_EXPIRATION:86400000} # 24 hours in milliseconds
- Rate Limiting:
Add rate limiting to prevent brute force attacks:
@Configuration
class RateLimitConfig {
@Bean
fun customKeyGenerator(): KeyGenerator {
return KeyGenerator { request ->
val ip = request.remoteAddr
val path = request.requestURI
"$ip:$path"
}
}
}
- Request Logging:
Implement request logging for security monitoring:
@Component
class RequestLoggingFilter : OncePerRequestFilter() {
override fun doFilterInternal(
request: HttpServletRequest,
response: HttpServletResponse,
filterChain: FilterChain
) {
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
filterChain.doFilter(request, response)
val duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
logger.info(
"Request completed: method=${request.method}, uri=${request.requestURI}, " +
"status=${response.status}, duration=${duration}ms"
)
}
}
Testing the Implementation
Here's a test class to verify our JWT implementation:
@SpringBootTest
class JwtServiceTest {
@Autowired
private lateinit var jwtService: JwtService
@Test
fun `should generate valid JWT token`() {
val userDetails = User(
email = "[email protected]",
password = "password",
roles = setOf("ROLE_USER")
)
val token = jwtService.generateToken(userDetails)
assertThat(jwtService.validateToken(token, userDetails)).isTrue
}
}
Conclusion
You now have a production-ready JWT authentication system implemented in your Spring Boot Kotlin application. This implementation includes:
- Secure user registration and login
- JWT token generation and validation
- Refresh token functionality
- Rate limiting
- Security logging
- Best practices for production deployment
Remember to:
- Regularly rotate JWT secrets
- Monitor failed authentication attempts
- Keep dependencies updated
- Implement proper error handling
- Use HTTPS in production
- Set appropriate token expiration times